When it feels like something is stuck in your ear, it can be frustrating and unsettling. Whether it’s a sensation of fullness or an actual inability to hear properly, a plugged-up ear can be caused by several different factors.
The ear is a delicate organ, and many things can lead to the feeling of blockage, from simple earwax buildup to more complex medical conditions. Knowing the potential causes of ear congestion can help pinpoint the issue and find the right solution.
Common Causes of Ear Congestion
1. Earwax Buildup
One of the most common reasons your ear might feel plugged is the accumulation of earwax, also known as cerumen. This natural substance helps protect the ear canal by trapping dirt, dust, and other foreign particles. However, sometimes too much earwax can accumulate, causing a blockage that leads to a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
How earwax buildup happens:
- The ear canal is lined with tiny hairs that help move earwax out of the ear. When these hairs are overwhelmed or malfunction, earwax can build up, causing a blockage.
- Overuse of cotton swabs can also push wax deeper into the ear, increasing the likelihood of a blockage.
The result is often a feeling of muffled hearing, discomfort, or even ear pain. In severe cases, earwax buildup can lead to ear infections or dizziness.
2. Sinus Congestion
Sinus issues, like a cold or allergies, can lead to ear congestion. When the sinuses are congested, the pressure in the sinuses can affect the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the nose and throat. These tubes help regulate ear pressure and drain fluid from the middle ear. If the Eustachian tubes become blocked, it can lead to a sensation of fullness or plugging in the ear.
What causes sinus-related ear blockage?
- Colds and Flu: Viral infections can lead to sinus congestion and swelling, which can then affect the Eustachian tubes.
- Allergies: Pollen, dust, or pet dander can cause inflammation in the sinuses, leading to ear pressure.
- Sinus Infections: Infections of the sinuses can result in fluid buildup in the ear, causing blockage.
Typically, sinus-related ear congestion is accompanied by other symptoms like a stuffy nose, headache, or pressure in the face.
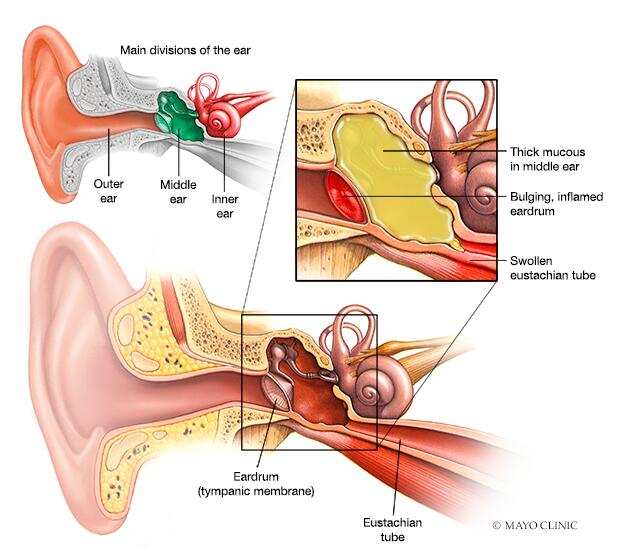
3. Fluid in the Ear
Sometimes fluid can accumulate in the ear due to various reasons, including infections or a buildup of mucus from sinus issues. This fluid can make it feel like the ear is plugged up. If the fluid becomes infected, it can lead to an ear infection, commonly known as otitis media. This condition is especially common in children but can affect adults as well.
Causes of fluid buildup in the ear:
- Ear Infections: These infections can result in fluid production in the middle ear, leading to a feeling of fullness or blockage.
- Swimming or Showering: Water can sometimes get trapped in the ear, particularly after swimming or bathing, which may cause temporary ear congestion. This is often referred to as “swimmer’s ear.”
- Eustachian Tube Dysfunction: If the Eustachian tube isn’t draining properly, it can lead to fluid accumulation in the ear, causing discomfort and a blocked feeling.
4. Changes in Air Pressure
Another common cause of ear congestion is changes in air pressure, often experienced during activities like flying, scuba diving, or driving through mountains. This is because the Eustachian tubes, which are responsible for equalizing pressure in the middle ear, can struggle to adjust to rapid pressure changes, leading to discomfort or a plugged feeling.
When does this happen?
- Flying: As the plane ascends or descends, the rapid change in altitude can cause a pressure imbalance between the middle ear and the environment, leading to ear congestion.
- Diving: When scuba diving or snorkeling, changes in underwater pressure can similarly affect the ears.
- Driving in Hilly Areas: In some cases, the change in altitude while driving through mountainous terrain can cause similar symptoms.
This kind of ear congestion is usually temporary and can be alleviated by yawning, swallowing, or using a special maneuver called the Valsalva maneuver, where you pinch your nose and gently exhale.
5. Infections
Ear infections can cause significant ear congestion, and they often come with symptoms such as pain, drainage, and fever. There are two primary types of ear infections that can lead to a plugged ear:
- Otitis Externa (Outer Ear Infection): This is an infection of the outer ear canal, often caused by bacteria or fungi. It can result in itching, redness, swelling, and a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
- Otitis Media (Middle Ear Infection): This type of infection affects the middle ear and is typically caused by bacteria or viruses. It can cause fluid buildup, pressure, pain, and a blocked sensation in the ear.
Ear infections are more common in children, but adults can also experience them. They often require medical treatment with antibiotics or other medications, especially if the infection is caused by bacteria.
6. Allergies
Allergic reactions can lead to ear congestion, particularly if you suffer from seasonal allergies. Pollen, mold, dust mites, and pet dander can trigger allergic reactions that cause inflammation and swelling in the nasal passages and Eustachian tubes. This can make it difficult for the tubes to drain fluid properly, resulting in ear congestion.
How allergies cause ear blockage:
- Nasal Congestion: Allergies can lead to swelling in the nasal passages, making it harder for the Eustachian tubes to function normally.
- Inflammation of the Eustachian Tubes: Swelling in the Eustachian tubes prevents them from opening properly, leading to a feeling of fullness or pressure in the ears.
If allergies are the cause, symptoms like sneezing, runny nose, itchy eyes, and sinus pressure may accompany the ear congestion.
7. Tinnitus and Hearing Loss
Although tinnitus and hearing loss are not causes of ear blockage, they can sometimes be associated with a plugged ear sensation. Tinnitus refers to the ringing, buzzing, or hissing sounds heard in the ear, and while it doesn’t directly cause a plugged feeling, the two conditions can overlap. Similarly, sudden or gradual hearing loss can sometimes make it feel like the ear is blocked.
When tinnitus and hearing loss are involved:
- Tinnitus: The persistent ringing or buzzing sounds in the ear may lead to the sensation of a blocked ear.
- Hearing Loss: Whether from age-related hearing loss or other factors, diminished hearing ability may make sounds seem muffled or distant, contributing to the feeling of a plugged ear.
8. Jaw or Teeth Problems
In some cases, jaw or dental issues can lead to ear congestion. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jaw to the skull, is located very close to the ear. Problems with the TMJ, such as jaw misalignment or teeth grinding, can cause referred pain or a sensation of fullness in the ear.
How jaw problems contribute to ear congestion:
- TMJ Disorder: A misaligned jaw can affect the ear area, leading to pressure and discomfort.
- Dental Issues: Problems with the teeth, such as an abscess or tooth infection, can also cause ear pain or the sensation of fullness.
How to Relieve Ear Congestion
If your ear feels plugged, there are several steps you can take to alleviate the discomfort, depending on the underlying cause. Here are some effective ways to address ear congestion:
1. Clear Earwax Buildup
If earwax buildup is the issue, you can try using over-the-counter ear drops to soften the wax and help it clear. Alternatively, you can visit a healthcare provider to have the earwax safely removed.
2. Treat Sinus Congestion
If sinus congestion is causing ear blockage, treating the underlying condition is key. Nasal decongestants, antihistamines, or saline nasal sprays can help reduce inflammation in the sinuses and relieve pressure on the Eustachian tubes.
3. Fluid Drainage
For fluid in the ear, a doctor may recommend treatments such as warm compresses or prescribed medication if an ear infection is present. For swimmer’s ear or water trapped in the ear, tilting the head and gently pulling the earlobe can help release the water.
4. Adjust Air Pressure
For air pressure changes, simple maneuvers like yawning, swallowing, or using the Valsalva maneuver can help balance the pressure in your ears. If the problem persists, a doctor may recommend decongestants or other medications to help with pressure regulation.
5. Seek Medical Treatment for Infections
If you suspect an ear infection, it’s important to see a doctor. Depending on the cause, antibiotics or other treatments may be necessary to clear the infection and alleviate the ear congestion.
6. Manage Allergies
If allergies are contributing to your ear congestion, managing the allergies with antihistamines, nasal sprays, or avoiding allergens can help prevent the sensation of a plugged ear.
Conclusion: Why Is My Ear Plugged Up?
A plugged ear can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from earwax buildup to sinus issues and ear infections. In most cases, the blockage is temporary and can be relieved with the right treatment. However, if ear congestion persists or is accompanied by pain, fever, or other concerning symptoms, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes and taking the right steps, it’s possible to relieve ear congestion and restore normal hearing function.