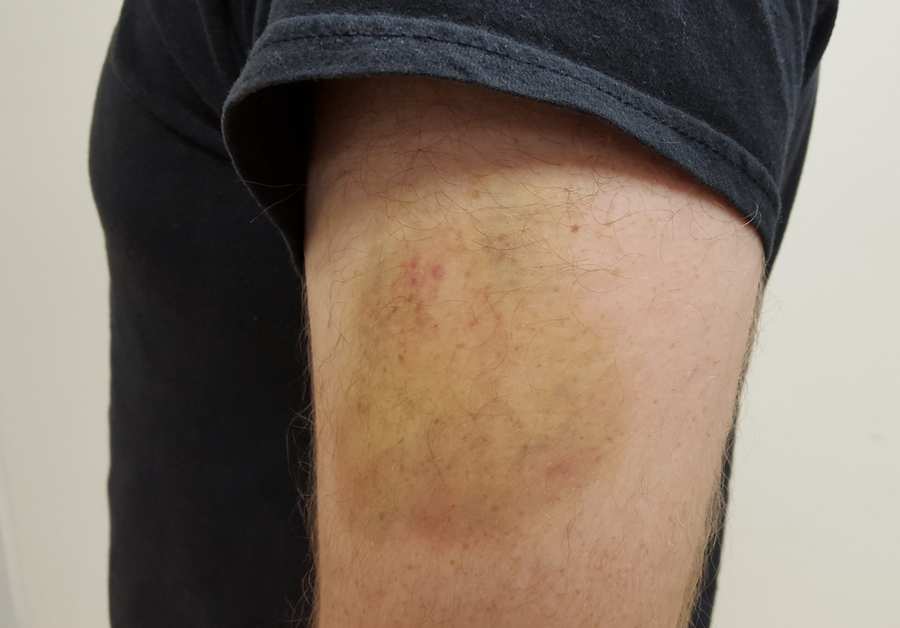
Hematomas typically last anywhere from a few days to several weeks, depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Understanding Hematomas: A Quick Overview
A hematoma is a localized collection of blood outside of blood vessels, usually resulting from an injury. When a blood vessel is damaged, blood leaks into the surrounding tissues, causing a raised, swollen area that can be painful to the touch. While hematomas are generally not life-threatening, they can be quite uncomfortable, and understanding how long they last can help manage expectations for healing.
Whether it’s a bump on the head, a bruise on your leg, or a deep tissue injury, hematomas can vary significantly in size, severity, and healing time. But how long does a hematoma last? The healing process can depend on several factors, including the severity of the injury, the location of the hematoma, and your overall health.
What Affects the Duration of a Hematoma?
Hematomas can last anywhere from a few days to several weeks, with mild injuries healing faster and more severe ones taking longer. Several factors can influence how long it takes for a hematoma to heal:
- Severity of the Injury
The severity of the injury is one of the most significant factors in determining how long a hematoma lasts. A minor injury where only a small amount of blood leaks into the tissues may resolve in a few days, while a more severe injury that causes more blood to pool under the skin can take longer to heal. - Location of the Hematoma
Hematomas that occur in certain areas of the body may take longer to heal due to increased blood flow or restricted drainage. For example, hematomas that occur on the head or near major blood vessels may take longer to heal than those on the arms or legs. - Age and Overall Health
Older adults and individuals with certain health conditions, such as diabetes or blood clotting disorders, may experience slower healing times. The body’s ability to repair itself declines with age, and conditions like diabetes can impede circulation, leading to longer recovery times. - Size and Depth of the Hematoma
Larger hematomas or those that occur deeper within the body typically take longer to heal. Deep tissue hematomas can cause more significant damage to surrounding tissues and may require medical intervention to resolve. - Treatment and Care
The way you care for your hematoma can also influence how long it lasts. If the injury is treated promptly and properly, healing can be accelerated. Applying ice, resting, and elevating the affected area can help reduce swelling and promote faster recovery.
The Healing Process: What Happens Inside Your Body?
A hematoma forms when blood vessels are damaged and blood leaks out into the surrounding tissues. This blood pools and forms a clot, which can cause swelling and bruising. Over time, the body works to break down and reabsorb the blood, leading to a reduction in swelling and the eventual disappearance of the hematoma.
Phases of Healing
- Inflammatory Phase (Days 1–3)
The first phase of healing begins immediately after the injury. Blood leaks from the damaged vessels into the surrounding tissues, causing swelling, redness, and pain. This phase usually lasts for 1–3 days and is marked by increased blood flow to the area, which is necessary for healing. - Resolution Phase (Days 4–10)
After the initial swelling and inflammation start to subside, the body begins to break down the blood clot. This phase typically lasts 4–10 days, and during this time, the hematoma may start to shrink as the body reabsorbs the blood. - Healing Phase (Weeks 2–4)
As the blood is gradually reabsorbed, the area of the hematoma may begin to feel less tender and the swelling will reduce. The bruising typically changes color, from dark purple or red to yellow or green, as the blood breaks down. By the end of this phase, the hematoma should be significantly smaller, and the pain and swelling will have reduced considerably. - Full Recovery (Weeks 4–6)
For larger or deeper hematomas, complete resolution can take several weeks. Even after the swelling and pain have subsided, it’s possible for some residual discoloration to remain, and the tissue may still feel a bit tender. Most minor hematomas heal completely within 4–6 weeks, though some severe cases may take longer.
Factors That Can Speed Up or Slow Down Healing
How to Accelerate Healing
While hematomas usually heal on their own, certain measures can help speed up the process:
- Rest and Elevation: Resting the affected area and keeping it elevated can help reduce swelling and improve circulation to the area.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice to the hematoma in the first 24–48 hours can help reduce swelling and prevent further blood from pooling.
- Compression: Gently wrapping the injured area with an elastic bandage can help reduce swelling. Be careful not to wrap it too tightly, as this could restrict blood flow.
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen, can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Always follow the recommended dosage.
- Heat Therapy: After the first 48 hours, you can switch to applying heat to the area to promote blood flow and help break down the blood clot more efficiently.
When Healing Is Delayed
Certain factors can slow the healing process:
- Poor Circulation: Conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, or peripheral artery disease can impair circulation and delay healing.
- Infection: If the hematoma becomes infected, the healing process can be delayed. Symptoms of infection include increased redness, warmth, swelling, and pus.
- Blood Disorders: Conditions like hemophilia, anemia, or thrombocytopenia can impair blood clotting and result in larger hematomas or delayed healing.
- Excessive Movement: If the affected area is constantly moved or stressed, it can interfere with the healing process and prolong recovery.
Types of Hematomas and Their Duration
Not all hematomas are the same. The location and severity of the injury can affect the duration of the hematoma’s healing process. Let’s look at a few common types of hematomas and how long they typically last.
1. Subcutaneous Hematoma
A subcutaneous hematoma occurs just under the skin, usually after a bump or fall. These types of hematomas are relatively shallow and can often be treated at home.
- Duration: 2–3 weeks
- Treatment: Rest, ice, and elevation
- Outlook: These usually heal fairly quickly, with the bruising disappearing over time.
2. Intramuscular Hematoma
An intramuscular hematoma occurs within the muscle tissue and may be caused by a muscle strain or direct blow. These can take longer to heal because the blood is trapped within muscle fibers, which can cause more pain and swelling.
- Duration: 3–6 weeks
- Treatment: Ice, compression, and possibly physical therapy for deeper injuries
- Outlook: The healing time depends on the size and depth of the hematoma, but with proper care, the swelling and pain should subside over time.
3. Epidural Hematoma
An epidural hematoma occurs between the skull and the dura mater (the outermost layer of the brain’s protective covering). It’s usually caused by a head injury and can be a medical emergency.
- Duration: Days to weeks (requires immediate medical attention)
- Treatment: Surgery may be needed to drain the blood and relieve pressure on the brain
- Outlook: Recovery time varies widely and depends on the severity of the injury and the promptness of treatment.
4. Subdural Hematoma
A subdural hematoma occurs between the dura mater and the brain tissue and is often caused by a head injury. It can be serious, especially in older adults, and requires medical attention.
- Duration: Weeks to months (depends on the size of the hematoma and treatment)
- Treatment: May require surgery or other medical interventions
- Outlook: Recovery can be slow, and the long-term prognosis depends on the size of the hematoma and how quickly it is treated.
Conclusion – How Long Does Hematoma Last?
The duration of a hematoma can range from a few days to several weeks, with most mild cases healing within 2–3 weeks. However, more severe or deeper hematomas may take longer, sometimes requiring up to 6 weeks or more to fully resolve. The key to a quick recovery is proper care, including rest, ice, elevation, and, when necessary, medical treatment. By understanding the factors that affect healing, you can better manage your recovery and know when to seek professional help if necessary.
With proper treatment and patience, most hematomas will heal completely, leaving only minor residual effects. If you notice signs of infection, significant pain, or delayed healing, it's important to consult a healthcare provider to ensure that there are no underlying issues prolonging the recovery process.