There is no cure for arthritis, but various treatments, including medications, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
Understanding Arthritis: A Chronic Condition
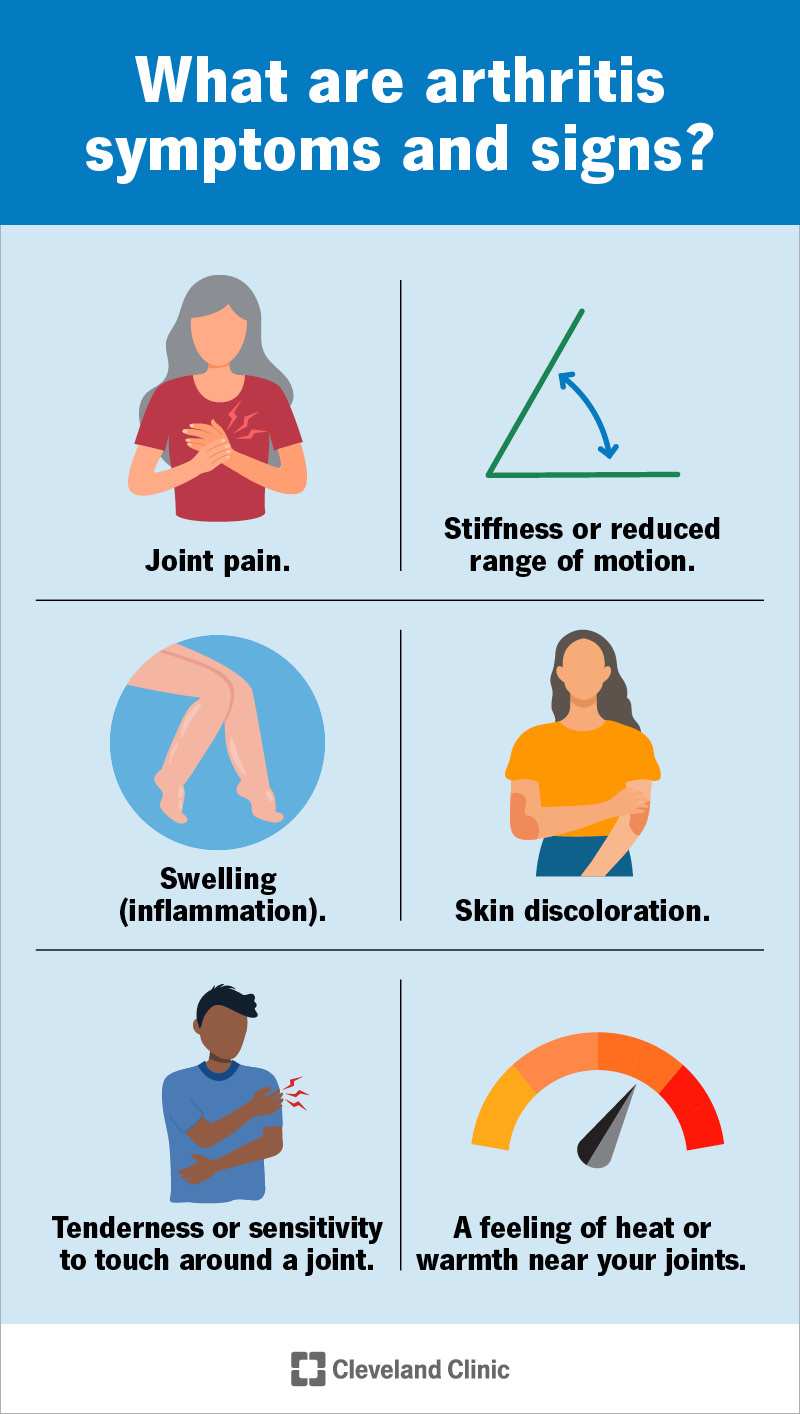
Arthritis is a term used to describe a group of more than 100 conditions that affect the joints, causing pain, swelling, stiffness, and reduced range of motion. It is a common condition that impacts millions of people worldwide, with osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis being the two most common types. While arthritis itself cannot be "cured," there are a variety of ways to manage the symptoms and slow the progression of the disease, allowing individuals to maintain their quality of life.
Living with arthritis can be challenging, but there are numerous strategies and treatments available to help alleviate pain, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility. From medication to physical therapy and lifestyle adjustments, there are many paths to managing arthritis. In this article, I’ll break down the various approaches to managing arthritis, including both conventional treatments and alternative therapies.
What Causes Arthritis?
Arthritis occurs when there is inflammation in the joints. The exact cause of arthritis depends on the type of arthritis in question, but in general, factors like genetics, age, sex, and lifestyle can all play a role in the development of the disease.
Osteoarthritis (OA)
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of arthritis. It occurs when the cartilage that cushions the joints begins to break down over time, resulting in pain and stiffness. OA typically affects older adults and is often related to the natural wear and tear that occurs with age. Joint injuries or obesity can also increase the risk of developing OA.
Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Rheumatoid arthritis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks healthy joint tissues, causing inflammation. Unlike osteoarthritis, RA can affect people at any age and can cause severe joint damage if left untreated.
Other Forms of Arthritis
There are many other types of arthritis, including gout, psoriatic arthritis, and juvenile arthritis, each with its own underlying causes and symptoms. Gout, for instance, is caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints, while psoriatic arthritis is associated with the skin condition psoriasis.
Can Arthritis Be Cured?
At present, there is no cure for arthritis. However, with the right treatments, it’s possible to reduce the severity of symptoms and slow the progression of the disease. Arthritis treatment aims to manage pain, improve joint function, and enhance the overall quality of life for those affected.
While conventional medicine offers various options for treating arthritis, a holistic approach that includes exercise, dietary changes, and stress management can also help manage symptoms.
How Do I Get Rid Of Arthritis? A Comprehensive Guide to Treatment
Although arthritis cannot be completely eliminated, there are several ways to manage the condition and reduce symptoms effectively. Here, I’ll break down the most common treatments used for managing arthritis.
Medications for Arthritis Relief
One of the first steps in managing arthritis is addressing pain and inflammation through medication. There are various types of medications used to treat arthritis, ranging from over-the-counter options to prescription treatments.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
NSAIDs are commonly used to treat both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. These medications help reduce inflammation and relieve pain. Some popular over-the-counter NSAIDs include ibuprofen (Advil) and naproxen (Aleve). While effective for short-term pain relief, long-term use of NSAIDs should be monitored closely due to potential side effects, including stomach ulcers and kidney problems.
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
DMARDs are primarily used to treat rheumatoid arthritis. These drugs work by targeting the immune system to reduce the inflammation that causes joint damage. Methotrexate is one of the most commonly prescribed DMARDs. While DMARDs can help prevent further joint damage, they may take several weeks to start working, and they can come with significant side effects, including liver damage and increased risk of infection.
Biologic Drugs
Biologic drugs are a newer class of DMARDs that target specific molecules involved in the immune response. Drugs like Humira and Enbrel are used to treat autoimmune-related arthritis conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis and psoriatic arthritis. Biologics are typically reserved for patients whose arthritis is not controlled by traditional DMARDs.
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroid medications, such as prednisone, are powerful anti-inflammatory drugs that can help manage arthritis symptoms. These are often used for short-term flare-ups or when other treatments are not effective. However, long-term use of corticosteroids can lead to side effects like weight gain, osteoporosis, and diabetes.
Physical Therapy and Exercise
In addition to medications, physical therapy is one of the most effective ways to manage arthritis. A physical therapist can guide you through specific exercises that help strengthen muscles around the affected joints, reduce pain, and improve flexibility. Regular physical activity can also help reduce joint stiffness and improve overall mobility.
Low-Impact Exercises
Low-impact exercises, such as swimming, cycling, or walking, are ideal for people with arthritis. These exercises help maintain joint flexibility without putting excessive strain on the joints. Regular exercise can also help with weight management, reducing the load on weight-bearing joints like the hips, knees, and lower back.
Stretching and Range-of-Motion Exercises
Stretching exercises can improve flexibility and reduce stiffness, especially in the morning when joints tend to feel stiffer. Incorporating gentle range-of-motion exercises into your daily routine can keep your joints flexible and prevent them from becoming too stiff over time.
Lifestyle Changes for Arthritis Management
Making changes to your daily routine can go a long way in managing arthritis symptoms. Here are some lifestyle adjustments that can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight
Excess weight puts additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce the pressure on your joints and ease pain. If you’re overweight or obese, losing even a small amount of weight can make a significant difference in the severity of arthritis symptoms.
Healthy Diet
A diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can help reduce joint pain and inflammation. Foods such as fatty fish (salmon, sardines), leafy greens, nuts, seeds, and berries are known to have anti-inflammatory properties. Omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, are particularly beneficial for managing arthritis symptoms.
On the flip side, it's best to limit processed foods, sugary snacks, and refined carbohydrates, which can contribute to inflammation and worsen arthritis symptoms.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can exacerbate arthritis symptoms by increasing inflammation in the body. Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga can help manage stress and reduce the impact of arthritis on your daily life.
Alternative Therapies for Arthritis
In addition to conventional treatments, many people with arthritis explore alternative therapies for symptom relief. While the effectiveness of these treatments varies from person to person, some may provide significant relief when used in conjunction with medical treatments.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture, a traditional Chinese medicine practice, involves inserting thin needles into specific points of the body to promote healing and relieve pain. Studies have shown that acupuncture can help reduce arthritis pain and improve joint function, particularly in cases of osteoarthritis.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Applying heat or cold to the affected area can help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. Heat therapy, such as warm baths or heating pads, can relax stiff muscles and improve blood flow. Cold therapy, such as ice packs, can numb the area and reduce swelling.
Herbal Supplements
Certain herbs and supplements are thought to have anti-inflammatory properties and may help with arthritis symptoms. Popular options include turmeric, ginger, and glucosamine. While these supplements may provide mild relief for some people, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, especially if you’re taking prescription medications.
Surgery: When Is It Necessary?
In some cases, when arthritis becomes severe and other treatments are no longer effective, surgery may be required. The goal of surgery is to relieve pain, improve function, and enhance quality of life. Surgical options for arthritis include:
- Joint Replacement: In cases of severe osteoarthritis, joint replacement surgery may be recommended, especially for the hips or knees. A damaged joint is replaced with an artificial one, helping restore movement and alleviate pain.
- Arthroscopy: This minimally invasive procedure involves using a small camera to inspect and treat damaged joint tissue. It’s often used to remove damaged cartilage or repair torn ligaments.
Conclusion – How Do I Get Rid Of Arthritis?
While arthritis can’t be completely cured, there are numerous effective treatments available to help manage the symptoms and slow the disease’s progression. A combination of medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and alternative therapies can provide significant relief from pain and inflammation. For those with more severe cases, surgery may be a viable option. The key to managing arthritis is finding a comprehensive approach tailored to your individual needs, allowing you to lead a healthy, active life despite the challenges the condition may present.