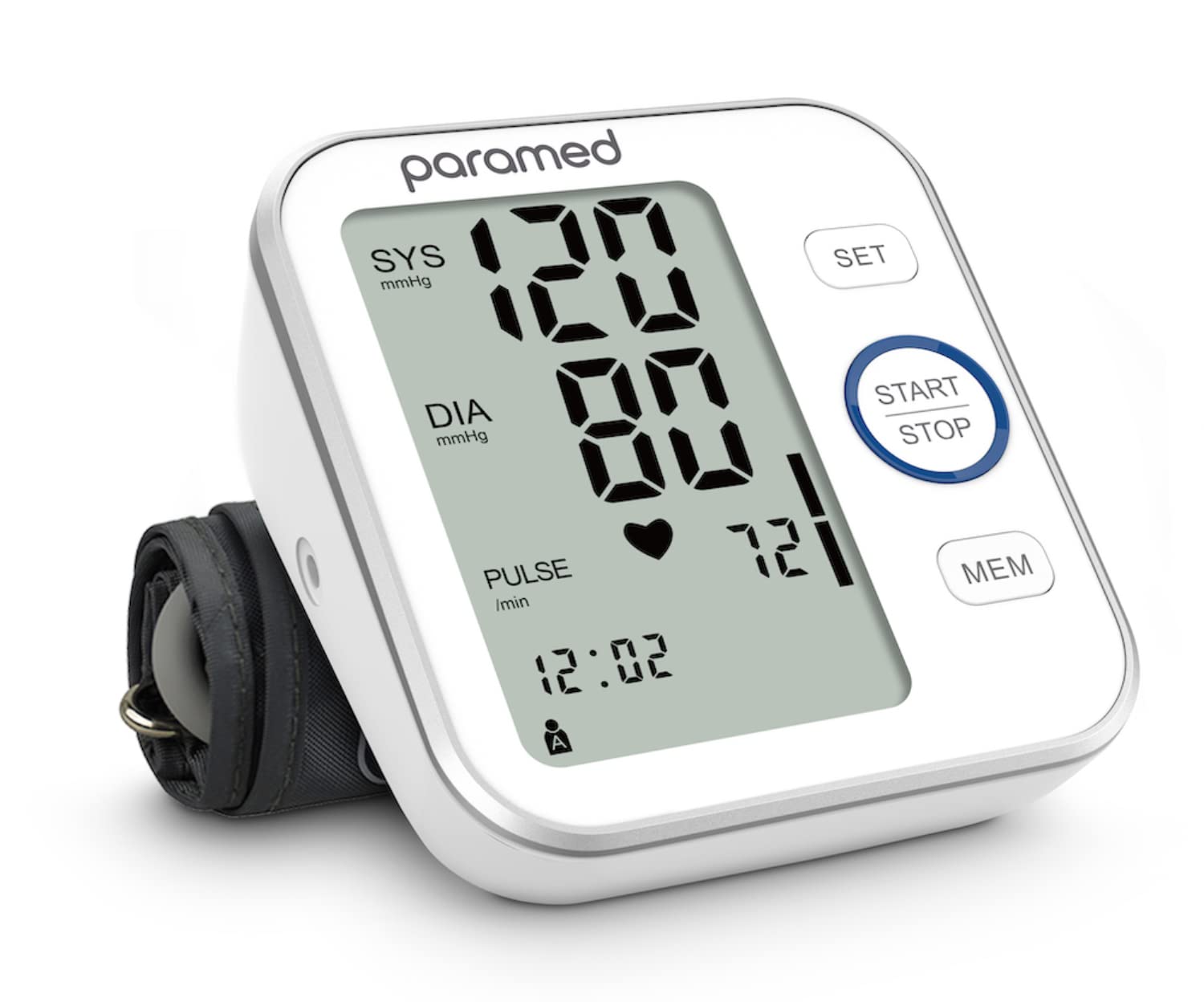
Blood pressure machines, or BP machines, can provide reliable readings, but their accuracy depends on factors like calibration, cuff size, and user technique.
Understanding BP Machines and Their Accuracy
Blood pressure (BP) machines are widely used tools for monitoring and managing blood pressure at home or in a healthcare setting. They offer a convenient way for individuals to track their blood pressure without needing to visit a clinic regularly. However, when it comes to their accuracy, many people wonder just how reliable these machines are. After all, accurate BP readings are crucial for diagnosing and managing conditions like hypertension.
In this article, we’ll dive into the various factors that affect the accuracy of BP machines, how they compare to professional measurements, and what you can do to ensure you're getting the most reliable readings. Whether you're using a digital or manual device, understanding the limitations and potential errors in BP measurement will help you trust the results more.
Types of BP Machines
Before we delve into the accuracy of BP machines, it's important to understand the different types available. BP machines generally fall into two categories: manual (aneroid) and digital.
1. Manual BP Machines (Aneroid Devices)
A manual BP machine uses a stethoscope and sphygmomanometer (the cuff) to measure blood pressure. The clinician inflates the cuff, then listens to the sounds of blood flow through the artery as the cuff deflates. These machines require expertise to get accurate results and are typically used by healthcare professionals.
2. Digital BP Machines (Automatic Devices)
Digital BP machines are more common for home use. They automatically inflate the cuff and use sensors to measure the pressure in the arteries as the cuff deflates. Results are displayed digitally on the machine’s screen, making them easier to use for individuals who are not trained healthcare providers.
Digital machines are popular due to their ease of use, but some users question their accuracy compared to manual devices.
3. Wrist and Finger BP Machines
While less common, wrist and finger BP machines have gained popularity due to their compact size and convenience. These machines work similarly to arm-based digital BP devices but are often considered less accurate due to the challenges of positioning and the anatomical differences between the wrist or fingers and the upper arm.
Factors Affecting BP Machine Accuracy
There are several factors that can influence the accuracy of BP readings, whether you're using a manual or digital machine. Here are some key ones to consider:
1. Cuff Size and Placement
The size of the BP cuff and how it’s positioned on the arm plays a critical role in getting an accurate measurement. A cuff that is too small or too large for your arm can lead to false readings. For example, a cuff that’s too small may result in a reading that’s artificially high, while a cuff that’s too large may give a reading that’s too low.
Proper placement is also important. The cuff should be positioned around the upper arm at the same level as the heart, with the center of the cuff aligned with the brachial artery. If the cuff is placed too high or low, the readings can be skewed.
2. Calibrations and Maintenance
Like all medical equipment, BP machines need to be calibrated regularly to maintain their accuracy. Over time, wear and tear can cause sensors in digital machines to become less precise. If you use a BP machine at home, it’s a good idea to have it calibrated periodically, especially if you notice inconsistent readings. Some manufacturers recommend having the device calibrated every one to two years.
For manual devices, regular calibration is also essential. While they’re generally more accurate than digital devices when used correctly, a miscalibrated aneroid device can still yield erroneous results.
3. User Technique and Consistency
How you use the BP machine can significantly impact the accuracy of the readings. Incorrect positioning, talking, or moving during the measurement can all lead to inaccurate results. To ensure the most accurate readings, follow these guidelines:
- Sit in a comfortable chair with your back supported and feet flat on the floor.
- Rest your arm on a table, keeping it at the level of your heart.
- Keep still and quiet during the measurement.
Inconsistent measurement practices can also lead to varying results. It's recommended to take multiple readings at different times of the day to get a more accurate picture of your blood pressure.
4. Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as room temperature and noise can also affect BP readings. For example, if the room is too cold, your blood vessels may constrict, leading to higher readings. Similarly, a noisy environment may prevent the accurate detection of the sounds of blood flow.
It’s best to measure your BP in a calm, quiet, and comfortable setting to avoid these environmental influences.
5. The Role of Technology in Digital BP Machines
Modern digital BP machines often come equipped with advanced technology, including sensors that help detect irregularities in your measurements and adjust for them. Some machines have arrhythmia detectors that can flag irregular heartbeats and provide additional information on your readings. However, while these features are helpful, they’re not foolproof, and it’s still important to monitor your results over time and consult with a healthcare professional if you have concerns.
6. Health Conditions and Medication
Certain health conditions, such as obesity, arterial stiffness, or pregnancy, can influence BP readings. For example, individuals with high body mass index (BMI) may find that a standard BP cuff isn’t sufficient to get accurate readings. For those with hypertension, readings may fluctuate based on factors like stress or medication.
Some medications, such as beta-blockers or vasodilators, can also impact blood pressure readings, sometimes causing fluctuations that may not reflect the actual state of your health.
Comparing Digital BP Machines to Manual Devices
While digital BP machines are often preferred for home use due to their simplicity, manual devices tend to be more accurate when used correctly by a trained professional. Here’s a quick comparison:
|
Feature |
Manual BP Machine (Aneroid) |
Digital BP Machine |
|
Ease of Use |
Requires expertise |
Simple and automated |
|
Accuracy |
More accurate with proper technique |
Can be less accurate due to user error |
|
Calibration Needs |
Needs regular calibration |
Needs periodic calibration |
|
Cost |
Typically more affordable |
More expensive, especially advanced models |
|
Portability |
Bulky and requires more setup |
Compact and portable |
Manual BP Machines
A manual BP machine is often seen as more accurate because it requires the operator to listen to the heartbeats using a stethoscope. This means that trained individuals can assess subtle variations in sound, making it easier to determine the exact BP reading. However, manual devices rely heavily on the operator’s skill and experience. Inaccuracies are more likely to occur in the hands of someone who is untrained or unfamiliar with the technique.
Digital BP Machines
Digital BP machines, while easy to use, are subject to greater variability in terms of accuracy. Some studies have shown that digital devices tend to overestimate systolic blood pressure, especially in older individuals or those with specific health conditions. That said, they’re generally reliable for routine monitoring of blood pressure and offer convenience, particularly for people who don’t have access to a healthcare professional regularly.
Ensuring Accuracy with BP Machines
To ensure that you get the most accurate readings from your BP machine, follow these steps:
1. Choose the Right Cuff Size
Make sure that the cuff is the right size for your arm. Most digital BP machines come with a standard-sized cuff, but some offer different sizes for larger arms. The cuff should fit snugly but not too tight, and it should be positioned correctly.
2. Check the Calibration
If you have concerns about the accuracy of your BP machine, consider having it calibrated by a professional. Some pharmacies or medical equipment stores offer calibration services. Regular calibration ensures that your device is functioning as it should.
3. Measure at Consistent Times
Blood pressure can fluctuate throughout the day, so it’s important to take measurements at consistent times. Try measuring your blood pressure at the same time each day, ideally after a few minutes of rest, and at least 30 minutes after eating or exercising.
4. Take Multiple Readings
Taking multiple readings can give you a more accurate picture of your blood pressure. Wait about 1-2 minutes between each reading to avoid artificially high results. You can then average the results to get a more reliable reading.
5. Use the Right Technique
Follow the guidelines for proper technique. Sit in a quiet room, with your arm supported at heart level. Avoid talking, moving, or crossing your legs while measuring your BP.
6. Monitor Trends, Not Just Individual Readings
One isolated high or low reading doesn’t necessarily mean you have hypertension. It's essential to track your blood pressure over time and identify any trends, as this gives a more accurate assessment of your cardiovascular health.
Conclusion – How Accurate Are BP Machines?
BP machines can be highly accurate when used correctly, but their performance depends on several factors. The calibration, cuff size, user technique, and measurement conditions all play crucial roles in the reliability of the results. While digital BP machines are convenient for home use, they may not always be as precise as manual devices. However, with regular maintenance, proper use, and consistency, BP machines can be a valuable tool in managing and monitoring blood pressure.