A typical glaucoma test can take anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes, depending on the type of test being performed.
Understanding the Glaucoma Test Process
Glaucoma is a serious eye condition that can lead to vision loss if left untreated. A routine glaucoma test is essential for detecting early signs of the disease, particularly since it often progresses without noticeable symptoms. For anyone getting tested for glaucoma, a common question is: How long does a glaucoma test take?
The answer varies slightly depending on the type of test your eye care provider conducts. Some tests are quick and simple, while others may take a bit longer. In this article, we’ll walk through the typical glaucoma test procedures, what you can expect, and how long each step may take.
Types of Glaucoma Tests
There are several types of glaucoma tests that your optometrist or ophthalmologist might use to check for signs of the disease. These tests assess different aspects of your eye health, including intraocular pressure (IOP), the condition of your optic nerve, and the drainage angle of your eye.
The two most common types of tests are the tonometry test and the ophthalmoscopy (or optic nerve evaluation), but your doctor may use additional tests based on your medical history and risk factors.
1. Tonometry: Measuring Eye Pressure
One of the first tests that doctors use to check for glaucoma is tonometry. This test measures the pressure inside your eye, called intraocular pressure (IOP). Elevated IOP is a major risk factor for glaucoma, though not everyone with high pressure will develop the condition.
How Long Does Tonometry Take?
Tonometry typically takes about 5 to 10 minutes. During this test, you may be asked to sit in a chair while the technician or doctor uses a device that either blows a small puff of air into your eye (non-contact tonometry) or lightly touches the surface of your eye with a small probe (contact tonometry). The device will measure how much resistance your eye has to the pressure.
While the non-contact version (air puff) is quicker and doesn’t require any numbing drops, the contact version may require you to first apply numbing eye drops to make the procedure more comfortable. Overall, the tonometry test is brief and non-invasive.
2. Ophthalmoscopy: Examining the Optic Nerve
After measuring eye pressure, your doctor will likely examine your optic nerve using ophthalmoscopy, which allows them to check for signs of damage caused by glaucoma. The optic nerve is the part of your eye that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. If glaucoma is present, it can lead to damage in this area.
How Long Does Ophthalmoscopy Take?
Ophthalmoscopy takes about 5 to 10 minutes. During this part of the exam, your doctor will dilate your pupils using eye drops. This makes your pupils larger so the doctor can see the optic nerve and the back of your eye more clearly.
The dilation process itself takes a few minutes, and once your pupils are fully dilated, the examination lasts just a few minutes. The doctor will use a special instrument called an ophthalmoscope, a small handheld tool with a light, to look at the back of your eye and examine the condition of the optic nerve.
Important Note on Dilation
After dilation, your vision may be blurry for a few hours, especially when trying to read or look at bright lights. You may also experience some sensitivity to light, so it’s a good idea to bring sunglasses to your appointment and have someone drive you home if necessary.
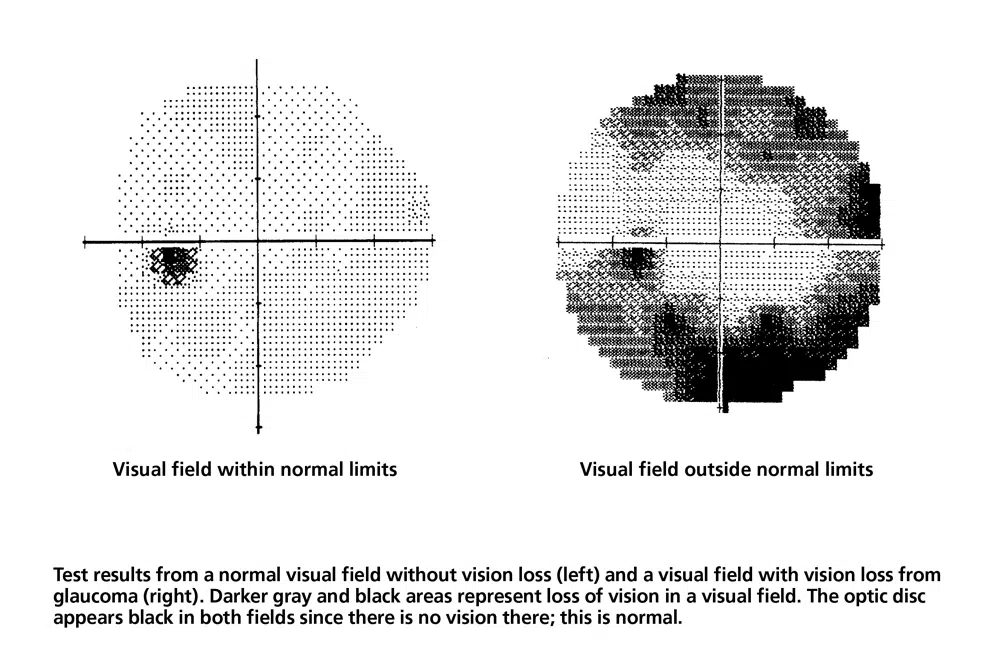
3. Perimetry: Testing Your Visual Field
Perimetry, also known as a visual field test, is used to check for any vision loss caused by glaucoma. Since glaucoma typically affects peripheral (side) vision first, this test helps detect any subtle vision changes before they become noticeable.
How Long Does a Visual Field Test Take?
The visual field test can take 15 to 20 minutes to complete. During this test, you’ll be asked to sit in front of a machine and look at a fixed target in the center of your vision. As the test progresses, lights or spots will flash in different areas of your peripheral vision, and you’ll need to click a button whenever you see one.
It’s important to focus on the center target and respond quickly. While the test doesn’t require physical exertion, it can be a bit tedious, as you’ll need to remain still and attentive for the duration of the test.
4. Gonioscopy: Checking the Drainage Angle
If your doctor suspects that you may have angle-closure glaucoma, they may perform gonioscopy to evaluate the drainage angle of your eye. This test helps determine whether your eye’s drainage angle is open or closed, which can affect the buildup of intraocular pressure.
How Long Does Gonioscopy Take?
Gonioscopy takes about 10 to 15 minutes. This test requires the use of a special contact lens that’s placed on your eye after applying numbing drops. The lens helps the doctor see the angle between the iris and the cornea, which is where the drainage system is located. The procedure is generally painless, but you may feel some pressure as the lens touches your eye.
5. Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT)
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is an advanced imaging test that creates detailed images of the optic nerve and the retina. This test helps detect early signs of glaucoma and other conditions by measuring the thickness of the retina and the optic nerve.
How Long Does an OCT Test Take?
An OCT test typically takes 10 to 15 minutes. During the procedure, you’ll be asked to look into a machine that takes detailed cross-sectional images of the layers of the retina. The test is painless, and no dilation is necessary. It’s a non-invasive way to monitor the health of your optic nerve over time.
Total Time for a Glaucoma Test
When combining all the above tests, a full glaucoma exam typically takes 15 to 30 minutes. However, if additional tests are needed, such as OCT or gonioscopy, the total time may extend beyond this range. Most people can expect their entire eye exam, including glaucoma tests, to take 30 to 45 minutes.
What Factors Can Affect the Duration?
- Type of tests: The more comprehensive the glaucoma exam, the longer it may take. If your eye care provider needs to perform multiple tests, such as tonometry, visual field testing, and gonioscopy, expect a longer visit.
- Pupil dilation: If dilation is needed, it can add an extra 10 to 15 minutes for the eye drops to take effect, which might slightly extend the overall time spent in the office.
- Technical difficulties: Occasionally, a test may take longer than expected if the machine experiences issues or if you have difficulty with a particular part of the exam, such as focusing during the visual field test.
Why Glaucoma Testing is Crucial
Even though the test itself may not take long, the benefits are invaluable. Early detection of glaucoma can make a significant difference in preserving your vision. If glaucoma is caught in its early stages, treatment options can prevent further damage and help you maintain your quality of life. Regular eye exams are especially important for those at higher risk for the disease, such as people over the age of 60, those with a family history of glaucoma, or individuals with other medical conditions like diabetes.
Conclusion: How Long Does a Glaucoma Test Take?
The duration of a glaucoma test varies, but typically it will take 15 to 30 minutes depending on the types of tests conducted. Routine tests like tonometry and ophthalmoscopy are relatively quick, while additional tests such as the visual field test or OCT may take longer. The overall process should take about 30 to 45 minutes, making it a quick but essential check-up for eye health. Regular glaucoma testing is key to catching the disease early and preventing vision loss, so it’s worth taking the time to prioritize your eye care.